Editor’s Note: The following article was written by Robert Young Pelton, a journalist, filmmaker, and the author of several books including The World’s Most Dangerous Places and Come Back Alive. His experience on the ground in the Libyan Civil War — including some serious close calls — reinforces the ever-increasing role combat drones play in wars and conflicts around the world.
Weaving our way through deserted back alleys, I can tell we’ve arrived at the front. Not just from the noise of heavy 14.5s, mortar hits, and RPGs, but because driver Hussam hunches down and peers up through the windshield of our grimy Toyota pickup. He’s looking for drones.
“Are you afraid of the drones?” I ask. “I am not afraid because I am putting my life for my country,” he answers.
I’m not totally buying it. Although the fighters I’m with are young, they’re well-seasoned. They fought in the 2011 Revolution, but now they really don’t have a plan on how to deal with this new threat. All while being partly encircled by the forces of General Khalifa Haftar.

Above: Hussam Elbakoush, of the Libyan Counter Terrorism unit points out a mortar hit.
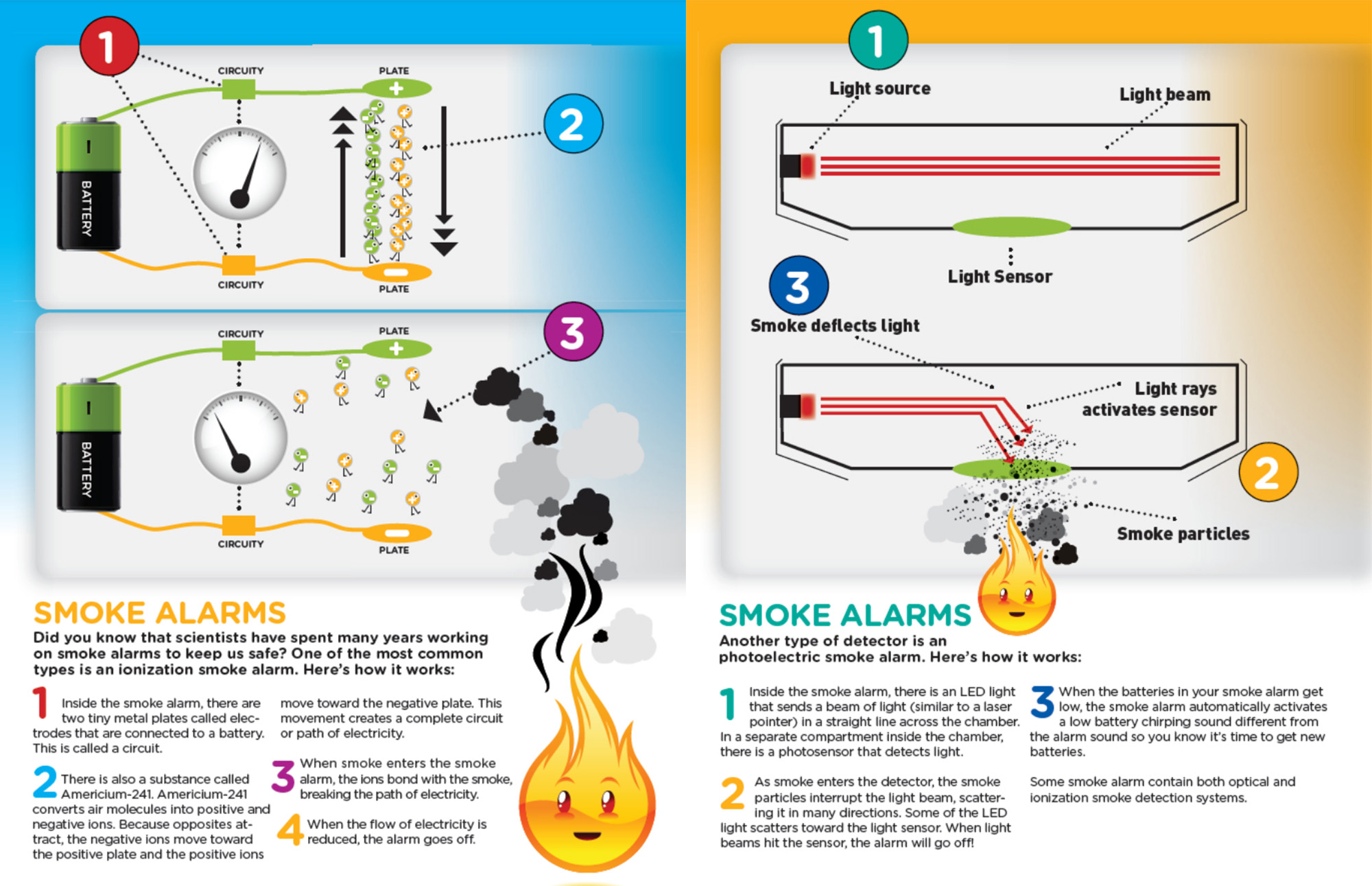
China’s Drone Industry
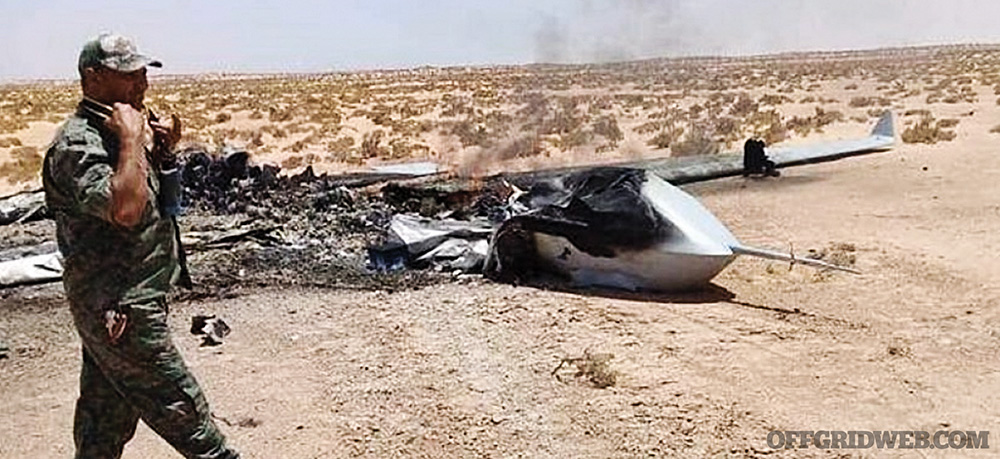
Haftar’s Libyan National Army (LNA) attacked Tripoli on April 4, 2019, and part of his arsenal included UAE-supplied Chengdu Pterodactyl II Wing Loong drones.
The medium-altitude long-endurance drones like the Wing Loong impart an impersonal feeling of Russian roulette to combat. Add to that Haftar’s hired mercenaries from Darfur and Russia and we’re in a new kind of soulless war — one where the combatants aren’t quite sure who’s killing them and those doing the killing aren’t quite sure who they’re killing. A perfect proxy war.

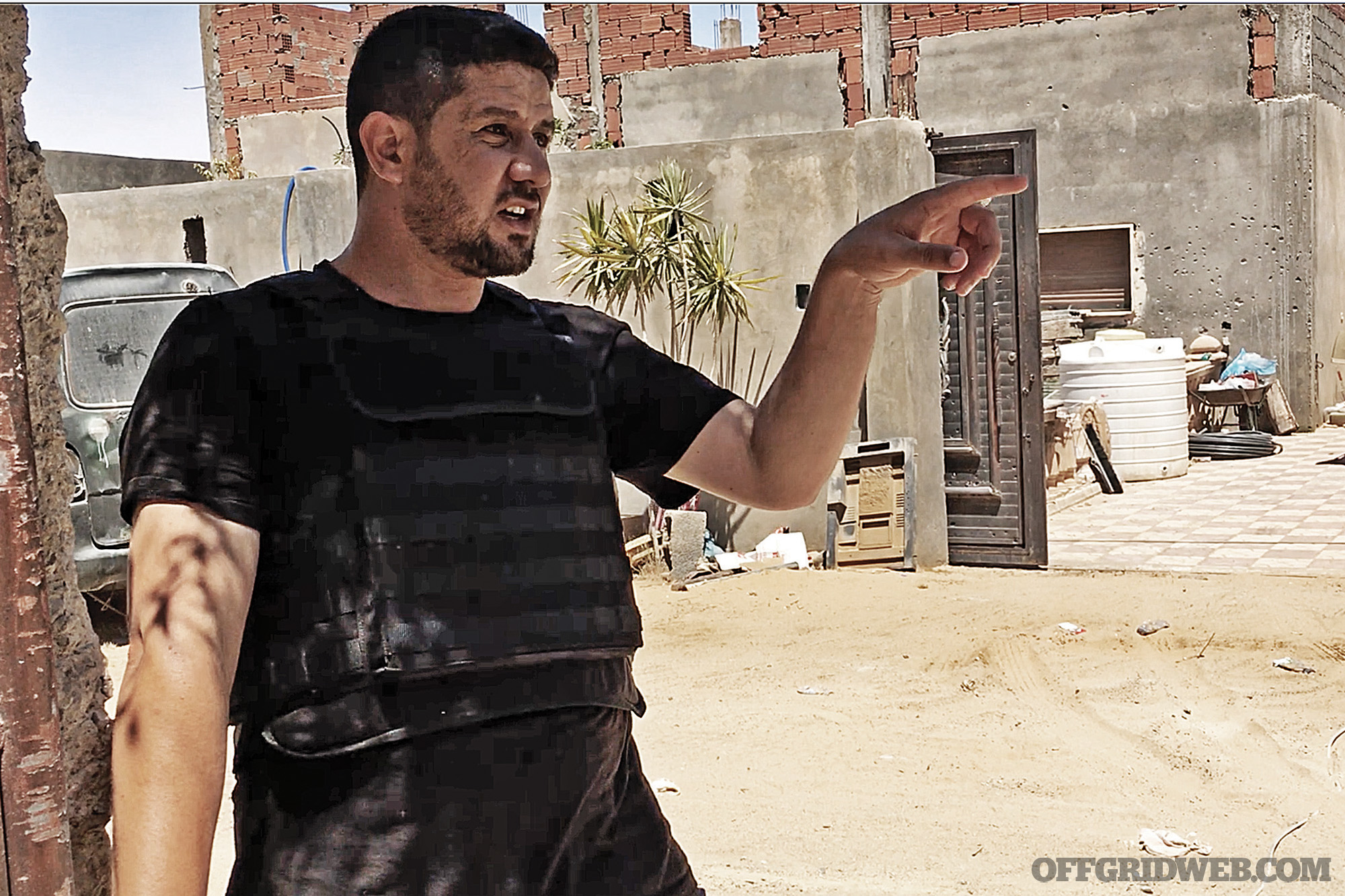
Above: LNA airstrikes on hospitals are common. This bomb missed and hit a yard of impounded cars.
The Wing Loong combat drones can fire eight Blue Arrow anti-tank missiles but are used against everything from pickups to civilians. They’re unabashed knockoffs of the American-made MQ-1 Predator and MQ-9 Reaper drones. At $1 million versus the $16 million price tag for the real thing, the Chinese (and countries like the UAE who “gift” them to Haftar) have made them very popular in dirty wars. The Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) estimates China sold 163 large, lethal UAVs to 13 countries between 2008 to 2018. But right now my driver and I are just worried about one.
The Wing Loong can fly at an altitude of around 5,000 feet for 20 hours. Their single 100-horsepower turbocharged engines sound a lot like lawn care equipment, only changing in pitch when they bleed altitude to fire. Right now, Haftar’s drone is searching above us for targets. The drone operator appears to get bored and moves off to surveil another front line.

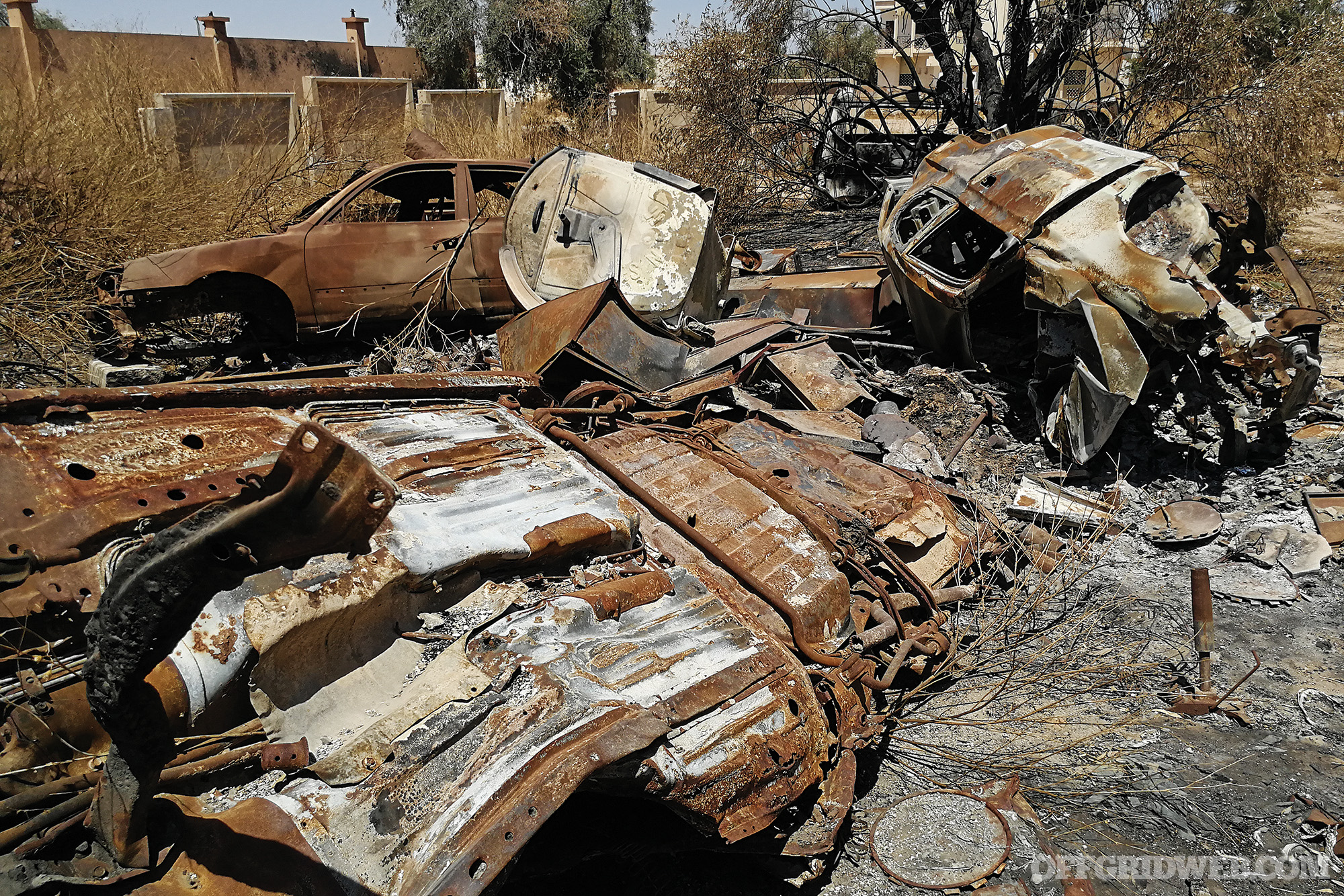
Above: At only a million dollars a copy compared to $14 million for U.S. versions, Chinese drones are cheap. Photo: Government of Libya
Another mortar hits one street over and interrupts our scan of the sky. We’re now focused on winding through back alleys, across yards, and through broken walls to get to our front line position. We engage in small talk while keeping an eye out for snipers.
Hussam has been to America, “Chicago, Indiana, and New York,” he exclaims proudly. “The people. They are so perfect. So kind.”
A War in the Suburbs
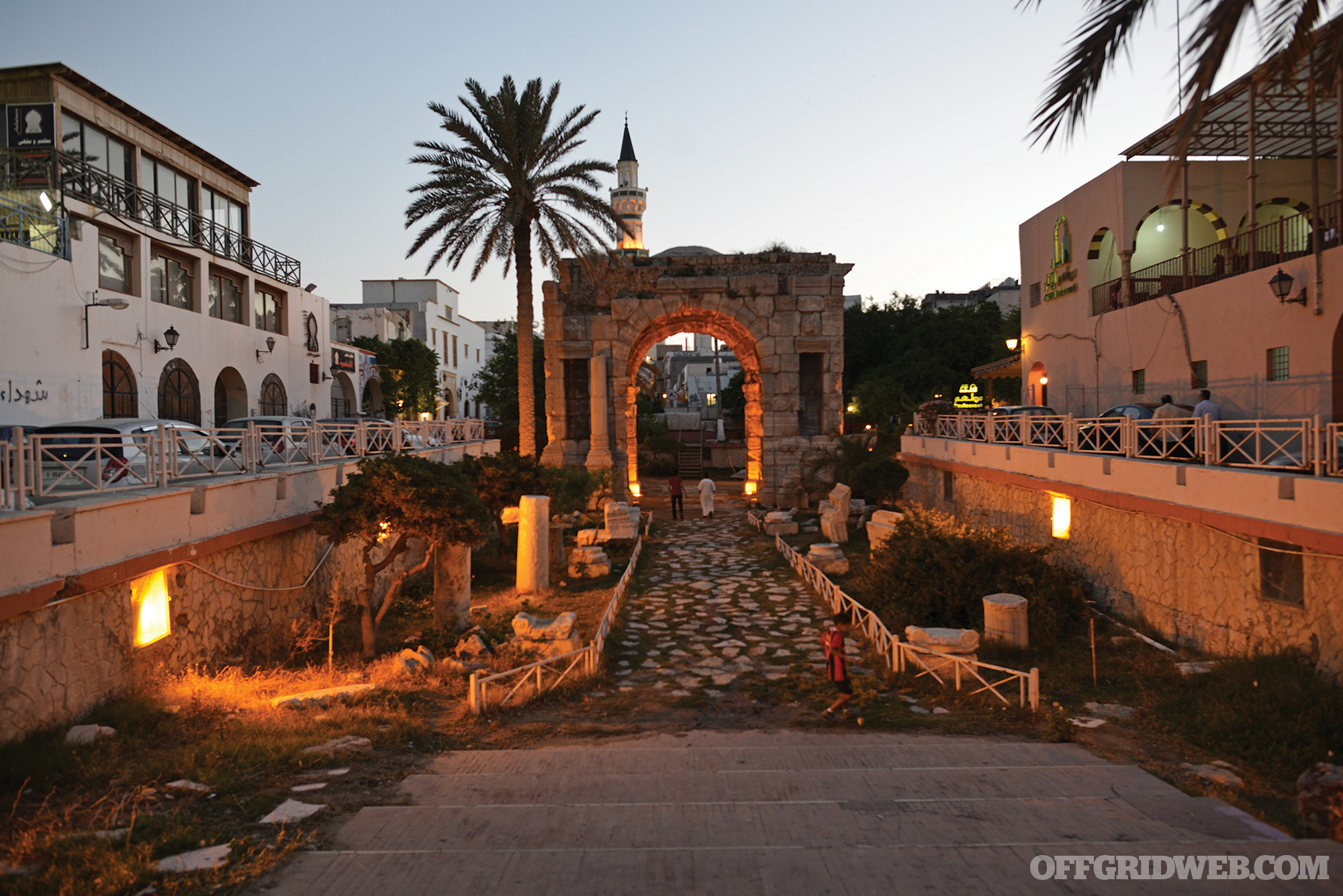

Above: The Arch of Marcus Aurelius, built in 165 AD, is a reminder of Libya’s historic links to Europe. The front lines are only 20 minutes away.
Hussam Elbakoush is a member of the Libyan Counter-Terrorism group. Not to be confused with the radical Islamist anti-terrorism police called RADA or the hundreds of militias who augment the official military in Libya. The GNA in Tripoli is propped up by RADA, the Tripoli Revolutionaries Battalion, the Nawasi Battalion, and the Abu Slim unit of the Central Security Apparatus. The GNA actually buys its munitions from the Katibas or militias because even the official government is covered by the blanket UN Arms Embargo — which makes one wonder how this war continues with new, high-tech weapons.
The front lines at Ain Zara are a suburban neighborhood of freshly abandoned homes with small cinder block-walled yards. The nicely stuccoed homes are pocked with munition splatters and gouges and separated by orchards and sand.
Then, the buzzing is back. Like the kind of noise that pisses off rich people when the gardener shows up on Sunday. The drone is here. We scan the sky, but the glaring sun makes it hard to get a fix. Another mortar drops, this time about 100 yards away.
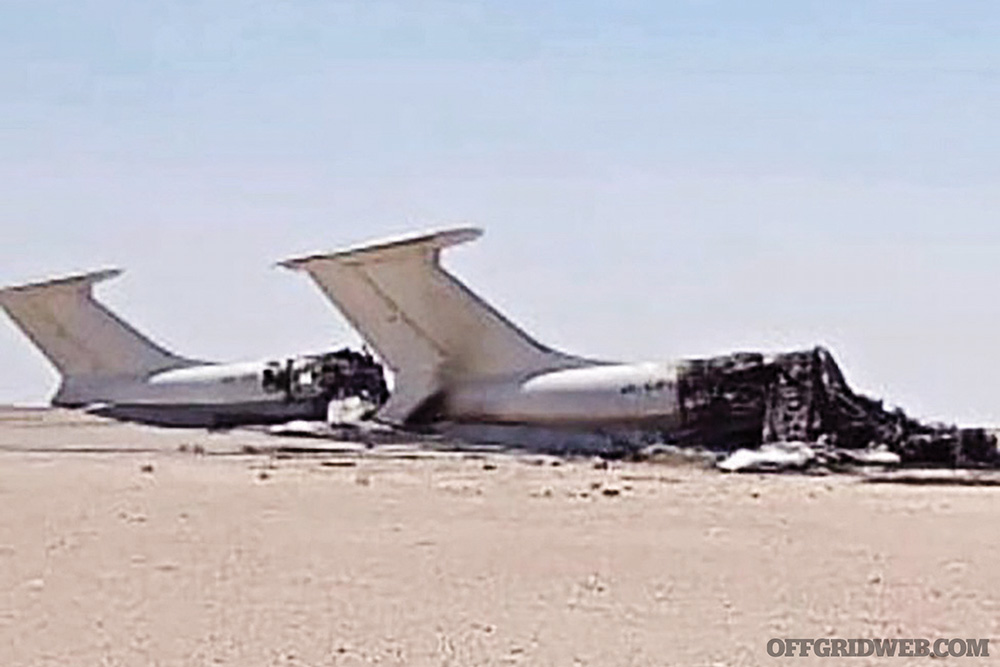

Above: Right: Two IL-76 taken out at al Jufra air base by Turkish drones.
Inside the house are half a dozen young fighters with various bits and pieces of uniforms. They have a sniper on the roof and keep their radios handy. The mortars are making them a little nervous. I tell them drones can target them by their cell phone and radio transmissions. They look at each other sheepishly. The idea of turning off your smartphone is silly. It’s their lifeline to the outside world. A place that pours psyops into their head while they keep in constant touch with friends and family, which also becomes a rich source of intel for real-time targeting.
Regardless, I suggest they shut off their phones. Then, of course, a ring tone emits from one of the fighter’s phones.

Above: If you know what to look for, you can find fresh meat.
Proxy Partners
Libya is one of the most developed nations in Africa, and it’s hard to understand why only 6 million Libyans can’t live comfortably off the shared oil revenue.
Peace and elections were something that seemed feasible until a 75-year-old American named Khalifa Haftar convinced the Emirati and Saudi rulers he could seize the capital of Tripoli and take control of the nation.
Flight records show that in early 2015, Haftar and crew were hopping between Tobruk, Egypt, UAE, and Saudi Arabia via a Malta-based Cessna Citation 550 9H-PAL (chassis number 550-0932) owned by Erik Prince’s Frontier Services Group. The goal was for the UAE to socialize the Qaddafist, former POW and ex-CIA asset as a potential strong man to take over Libya. This coincided with a February 2015 profile piece in the New Yorker by Jon Lee Anderson and an infusion of cash.
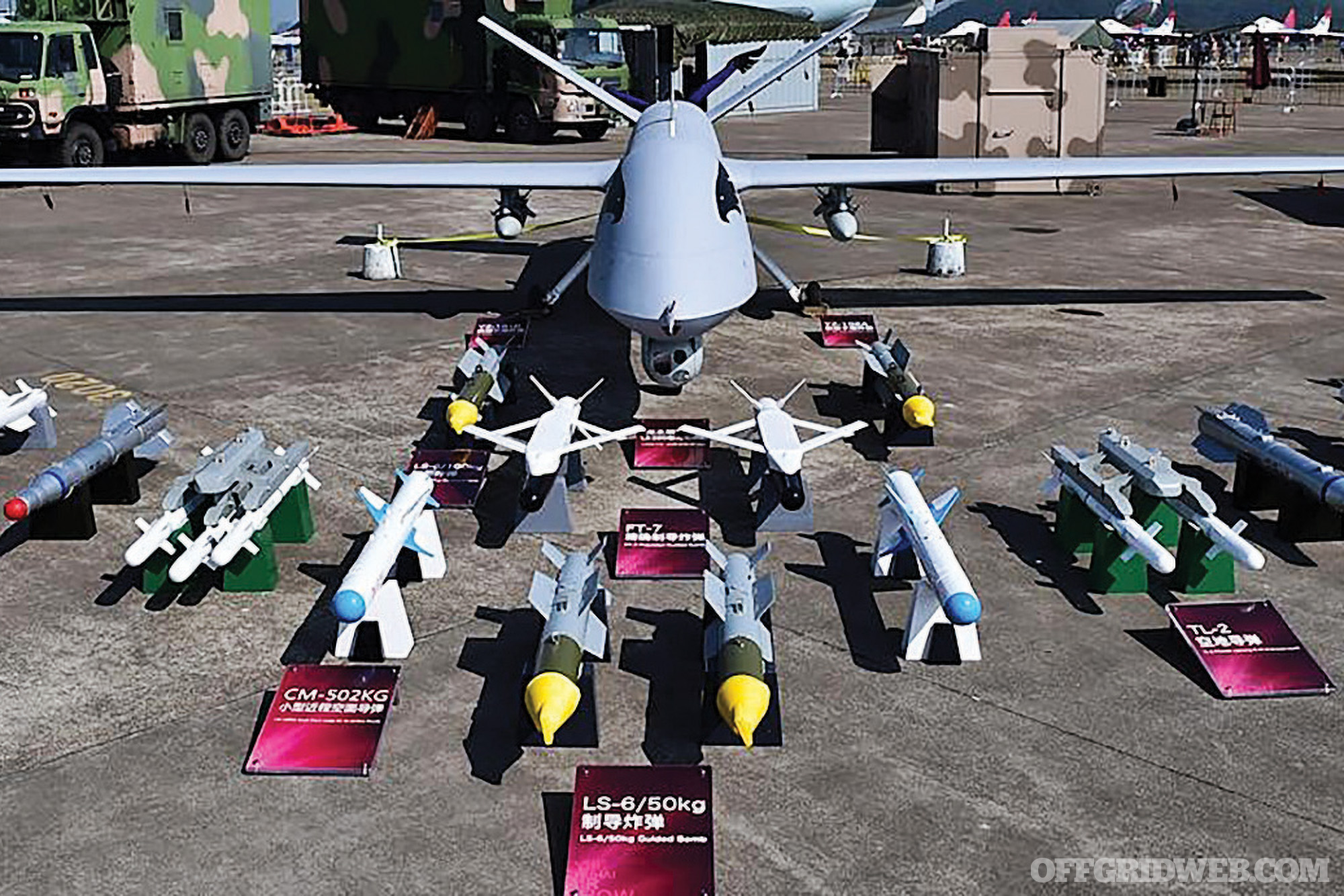

Above: The Chinese-made AVIC Wing Loong II drone is the poor man’s Reaper. Photo courtesy AVIC
It worked, and on March 2, Haftar was chosen to lead the LNA.
According to an intel officer from a wealthy Arab nation, Haftar asked the King of Saudi Arabia for a billion dollars to fight the war. The King said, half a billion will have to do. Waiting in his private jet, Haftar discovered that the $500 million had already shrunk to $350 million. Haftar wisely sent $300 million to Jordan with his two adult sons, Khalid and Saddam, to stash and tried to pay off the militias with only $50 million. So on April 5, 2019, Haftar and his forces attacked Tripoli … and surprise … it didn’t work. Some of Haftar’s overconfident forces led by Khalid weren’t only captured en masse, but met fierce resistance in South Tripoli from the very militias that were supposed to conveniently give up and hand the city over. Haftar was stuck. Since then, the LNA has ringed the south, east, and west of Tripoli and been stuck in a war of over-gunned Toyota technicals, badly trained militias, and drones.

Above: China’s best-selling aircraft is a lethal combat drone. Photo courtesy AVIC
The American Who Wants to Control Libya
In between interviews and trips to the front lines, I stay in the posh, eight-story Victoria Hotel. From my favorite evening table on the roof, the city of 2 million seems normal. Sort of. Tripoli is suffering from electricity and water cutoffs but stays illuminated by pools of light provided by hundreds of generators purring in the cool evening. People sit in groups, their faces glowing by the light of their smartphones. Trash sits uncollected, and Tripoli looks tired, but the citizens are defiant. To them, Haftar is an interloper, a mercenary who is well past retirement age, but someone who hasn’t been in Libya since he couldn’t find a role in the 2011 revolution and whose last official military job for Libya was being held as a prisoner of war by Chad in the late ’80s. You won’t find many Haftar supporters on the streets of Tripoli, if any.
Haftar’s forces had just fled the city of Gharyan a few miles south. Although I tried to drive in, I was sent back by militias due to the drone threat.
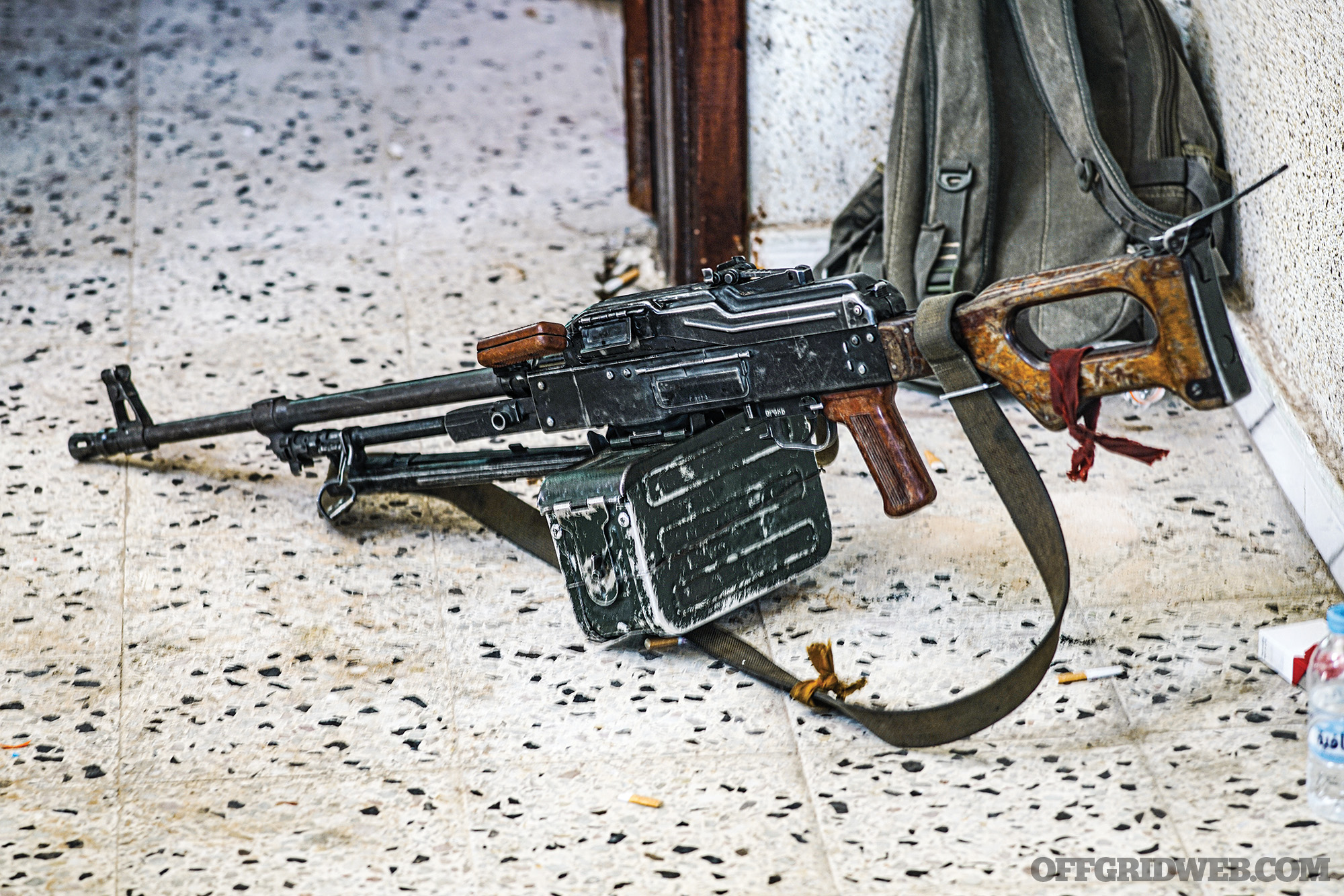

Above: The Pulemyot Kalashnikova, or PKM, is the favorite weapon on the front lines.
Instead, Gharyan Mayor Yousef Ibderi came to see me. We met on my hotel rooftop to explain how they flushed Haftar’s forces out. The young mayor tells me that after the LNA offensive was stalled, they set up their operations base in his town. So he organized a rebellion. Soon 80 men with their own weapons synchronized early in the morning and expelled the LNA.
“We just kept shooting at Haftar’s men until they fled in terror,” Ibderi recalls. Seems like the minuteman concept still works in Libya and is perhaps an omen of what would happen if the LNA and Haftar make it to Tripoli.
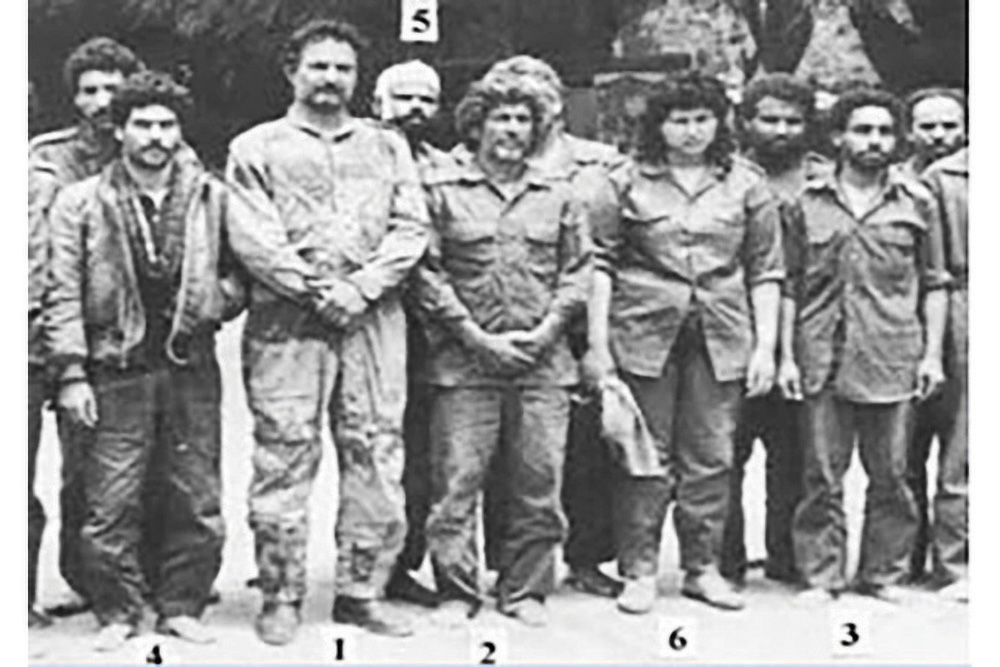

Above: In 1987, Colonel Khalifa Haftar and his massive army base at Wadi Doum were overrun in Chad. He was trained by the CIA to overthrow his friend Qaddafi. After some downtime in the DC suburbs, and with a little help and a lot of money from Arab kingdoms, he’s back. Photo: Government of Chad
Haftar isn’t one for hearts and minds. The hawk-faced resident of Falls Church, Virginia, turned-Libyan “Field Marshall” incessantly announces via social media that it’s “Zero Hour” for Tripoli. He makes these proclamations from his tiny bunker in Marj and his public relations spokesman, former actor and poet Colonel Ahmed al-Mismari, does his best impression of Baghdad Bob. There’s no Zero Hour, Tripoli isn’t falling, and Haftar isn’t winning. But, then again, neither is the GNA, crippled by the UN Arms embargo. Even the recent attempt by Turkey and Russia to broker peace talks ended up with Haftar storming out of Moscow because he was kept waiting. Nobody wins these kind of wars.
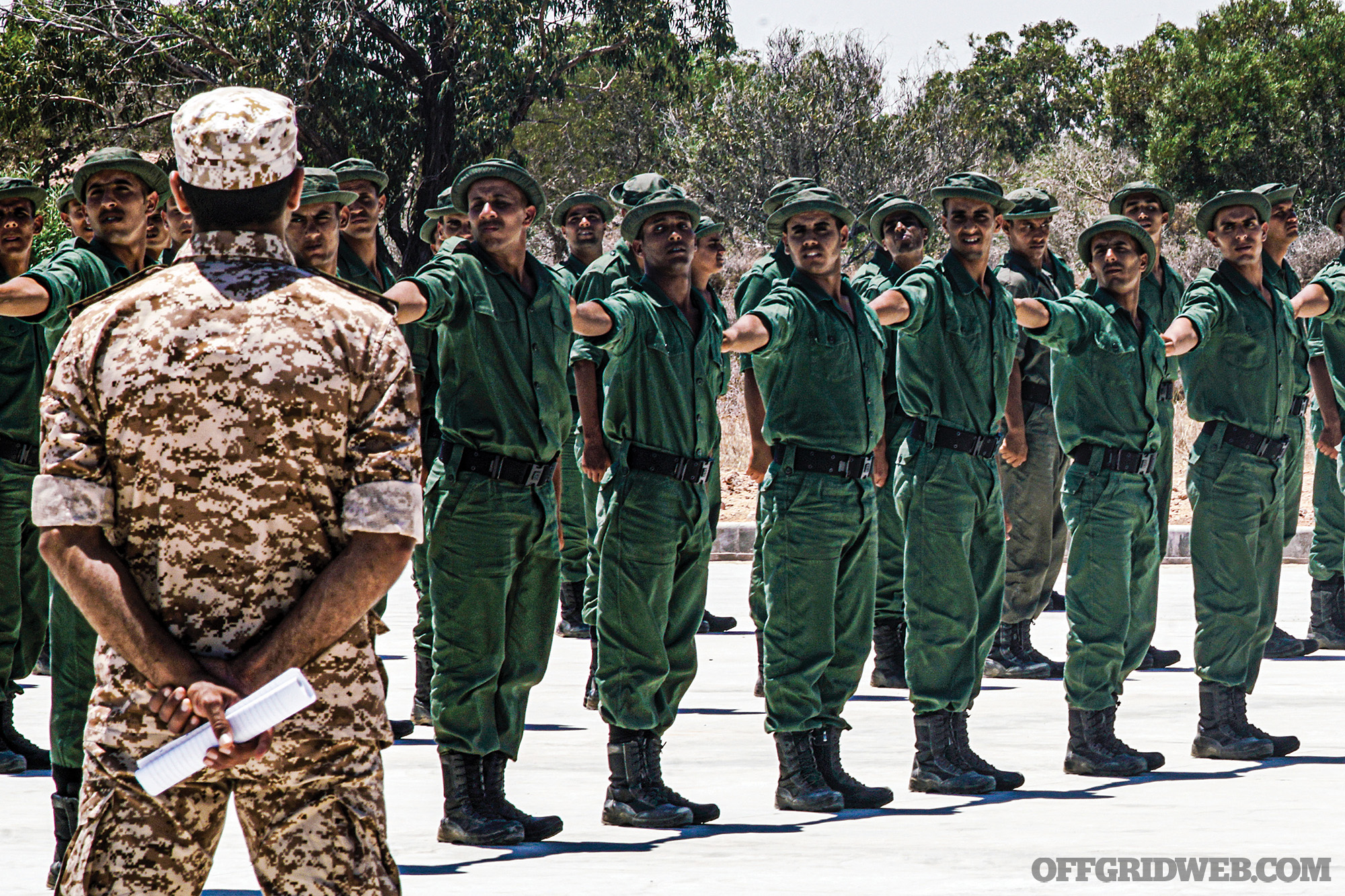

Above: Libya is slowly trying to rebuild their army, but for now, militias who fought the military in the 2011 revolution hold sway.
The reality is that life still goes on in Tripoli. Watching the deep red moon rising over the bay of Tripoli, suddenly explosions boom and echo through the dark streets, sending showers of sparks. It’s a war journalist’s dream come true — not even spilling your drink while covering the fight close up. But no, it’s not the long-awaited final “Zero Hour” attack on Tripoli, but rather badly aimed fireworks celebrating the Algerian soccer team’s victory in the African Cup. Perception and manipulation via social media is a big part of this war, as smartphones are the lifelines and major news coverage is rare.
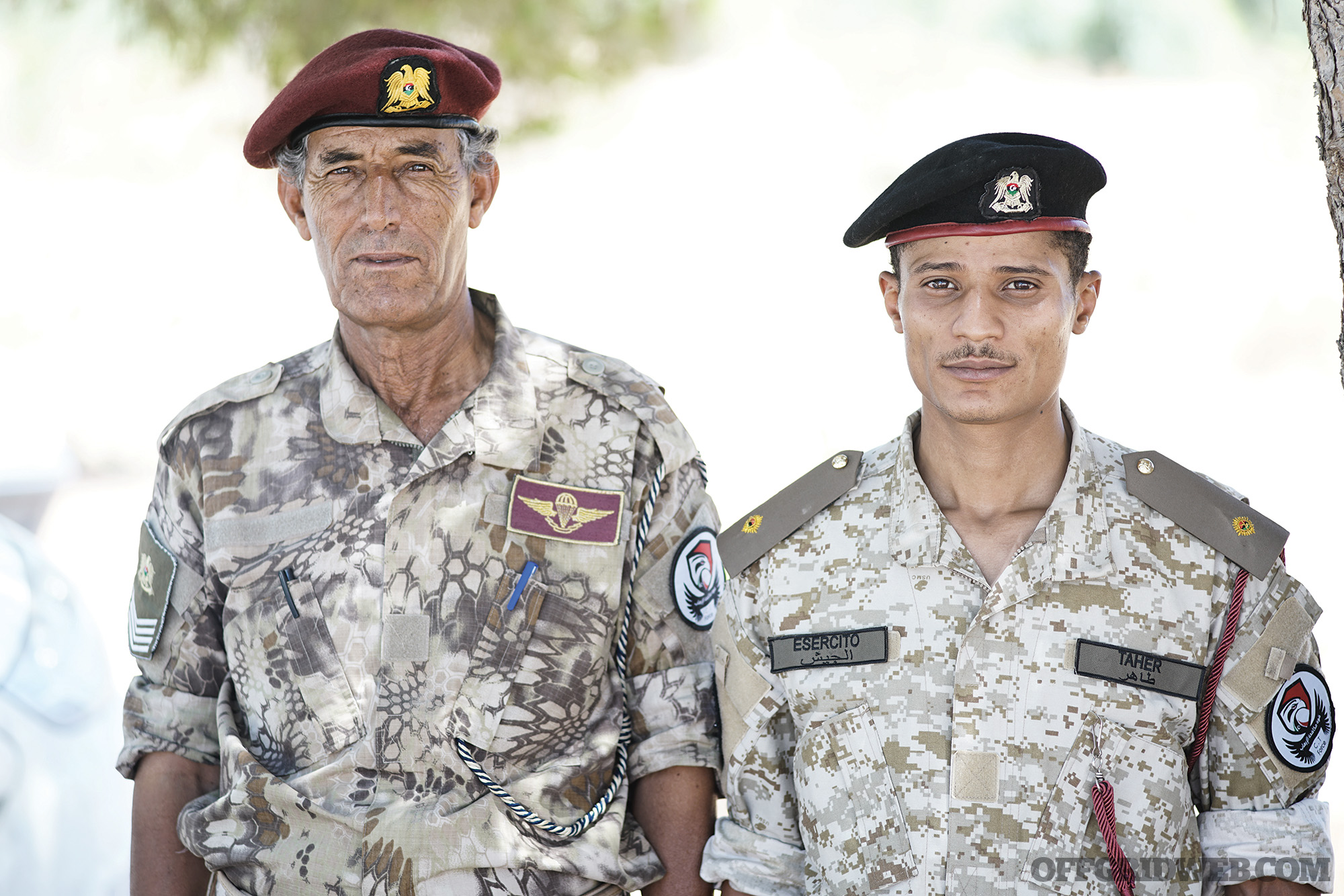

Above: Some of the old guard pass on skills to the new, but Chinese drones, UAE psyops, and electronic warfare are new to the Tripoli front lines.
The Nine-to-Five War
Despite the war, there’s no shortage of hospitality and conversation in Tripoli.
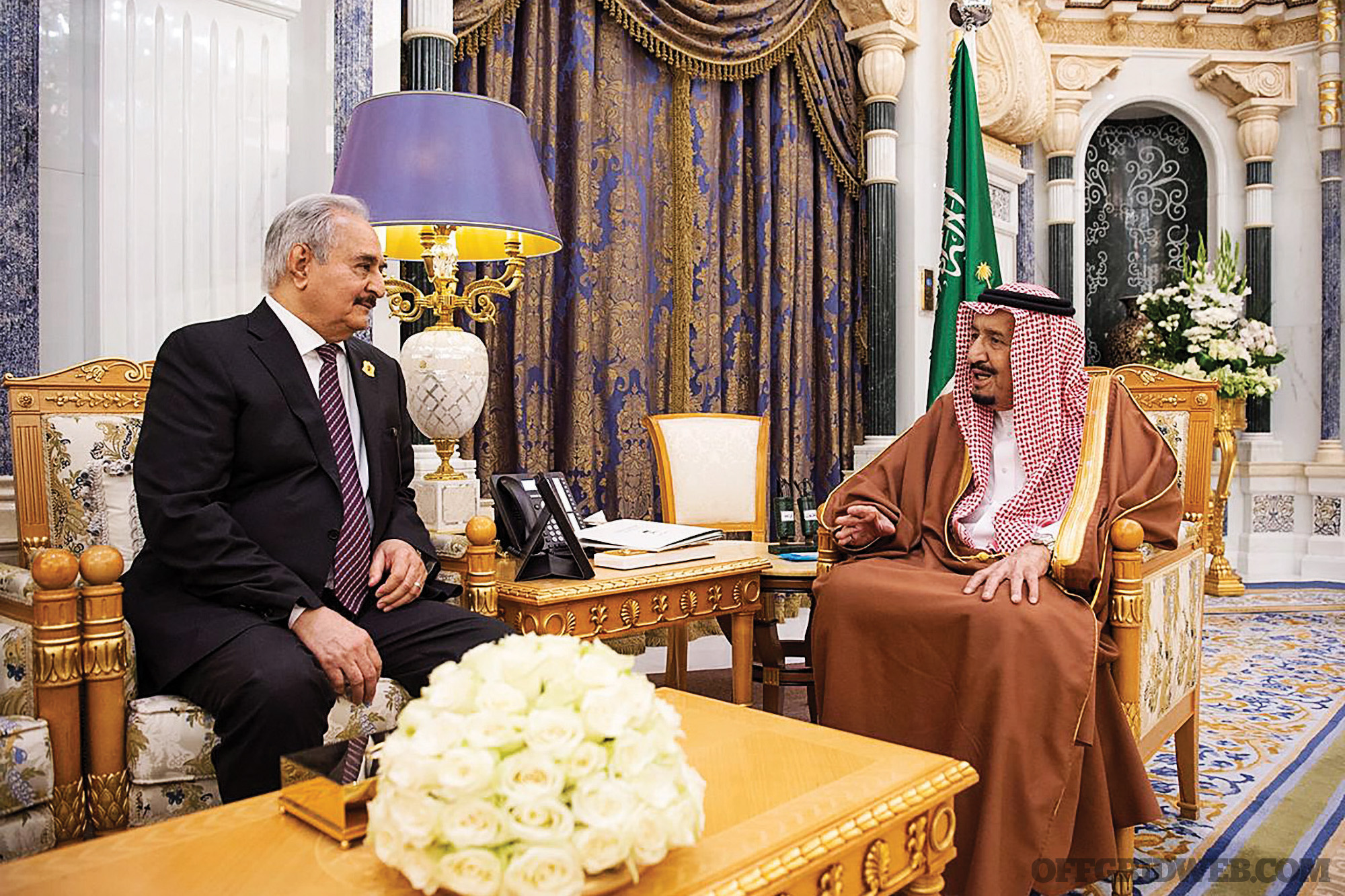

Above: Saudi Arabia’s King Salman bin Abdulaziz meets with Libyan military commander Khalifa Haftar in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia March 27, 2019, a week before Haftar attacked Tripoli. Photo: Saudi Press Agency
Retired military Colonel Suliman Sulewehi invites me out for a seaside lunch of freshly caught fish. After picking out our catch, he tells me, “This is a brother’s war.” Libyans are fighting Libyans at the behest of outsiders like the UAE and Saudi Arabia. He takes me through the history of Libya and interlopers. The Arabs, Knights of Malta, Ottomans, and Italians. “They were all kicked out,” he insists. Now he believes the old colonial powers and Arabs from the east want back in. He describes France’s role as “mischievous” supplying weapons while holding peace talks. “The Arabs (meaning the Emiratis, Saudis, and Egyptians) do not want stability.” He believes Libya is the rightful gateway to Africa, not the UAE. He takes me out to the front lines in Salluhudin, which is a surprisingly short ride as the traffic thins down to nothing. Suddenly, we’re the only people inside a military base.

rpt
Above: Mayor of Gharyan Yousef Ibderi explains how the townspeople forced Haftar’s forces out in eight hours.
Sulewehi says he helps support a small katiba of 145 men and 20 vehicles. They’re holding the line near Salluhudin, about 1,000 meters from Haftar’s army. He admits it’s hard. “Haftar fighters get paid more money, 2,000 dinars compared to only 1,000 dinars for his people.”
“They have little training, they know little of tactics,” he continues. It’s an odd irony that both sides are paid by the Libyan government, but it’s a reminder that Libyans see themselves as a single nation, however divisive their politics are.
The commander is a man in his 50s who was once involved in embassy security. He tells me his men need uniforms, rifles, and ballistic vests. He’s most concerned about the UAE-supplied drones.
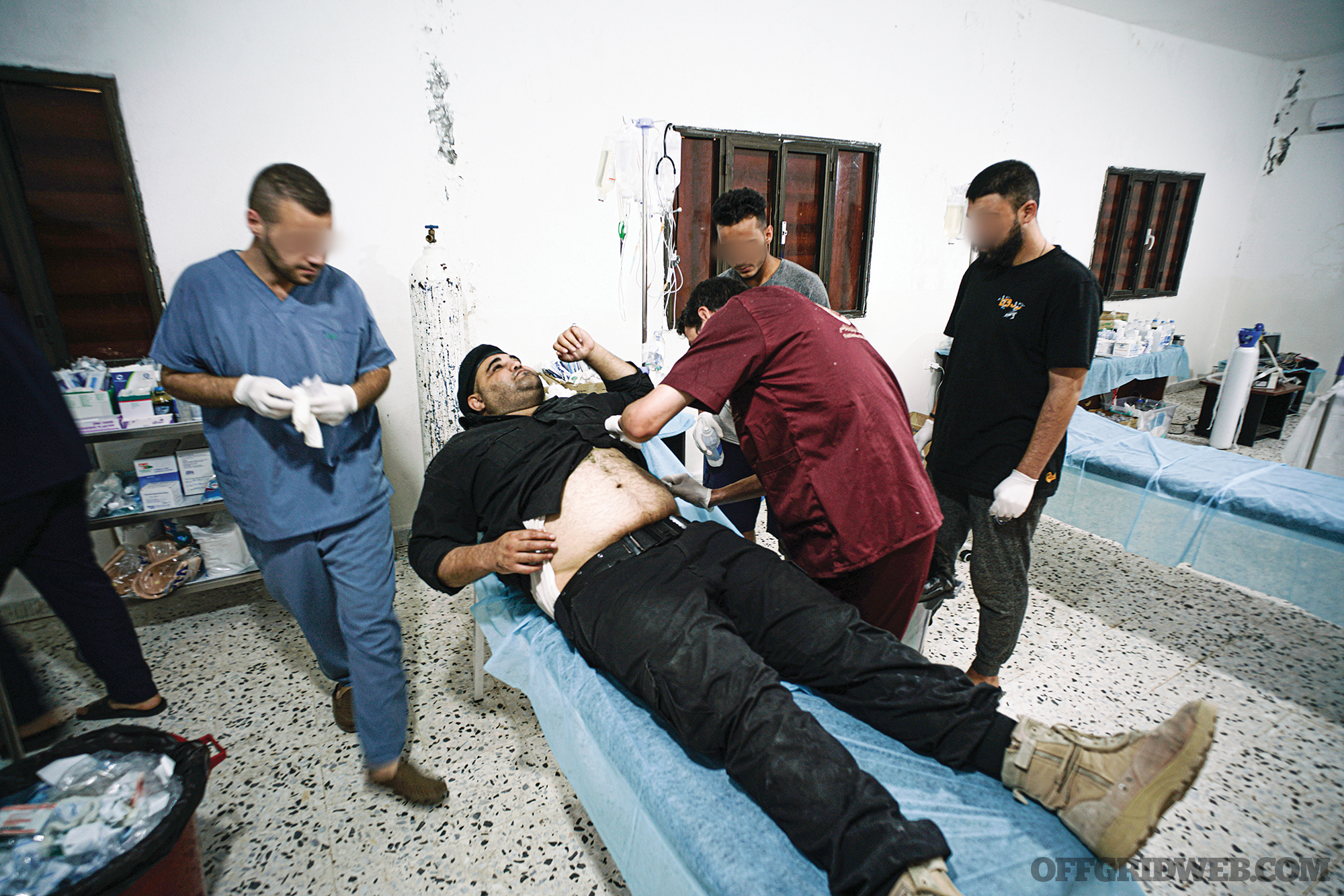
Above: Medics and doctors are routinely targeted by drone operators and in direct attacks.
“They are up every day and strike randomly at soldiers or medics,” he tells me. That day, the drones followed an injured fighter they had just hit until their vehicle arrived at a field hospital. When the medics came out with a gurney, the LNA drone operator fired again, killing two doctors.
The commander has no idea how to deal with drones except to hide their vehicles and spread them out. I ask if Libyans or Emiratis are deciding on targets. Without hesitation he says, “Libyans.” Why? “Because they are assholes and will shoot at anything.”
A Mortar Send-off
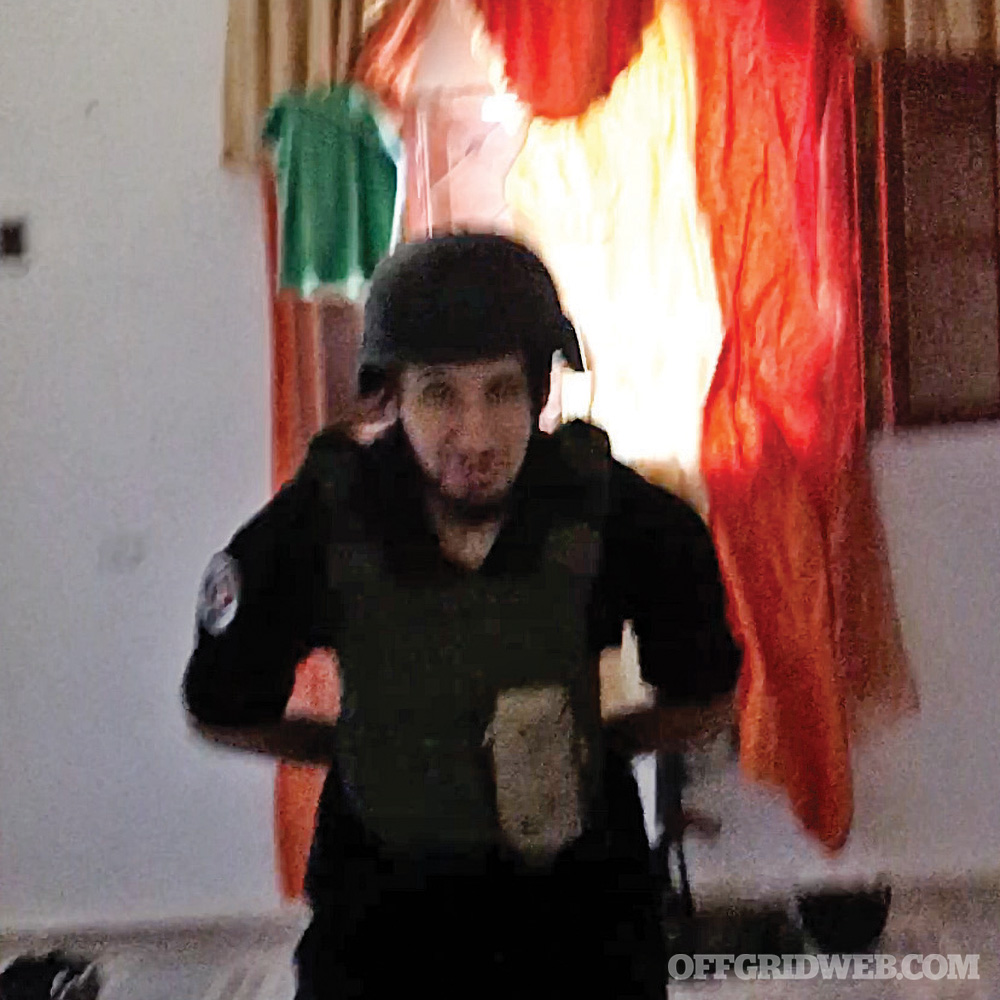

Above: Guided by a drone operator, another mortar hits outside our house.
It’s my last day in Libya and I have to catch a plane in the afternoon, so I spend the morning out on yet another front line. This time I’m being bracketed with mortars and watched by drones with Hussam Elbakoush. Everyone in the house is now in agreement with my thesis that the enemy is methodically moving each mortar strike slowly toward our house. Since spotters can’t see us, I figure they’re using a drone to target us. When another mortar lands on the street he motions me outside to the gate to take a photo. BAM. They almost get him with a quick mortar that lands on the street. Back inside, it’s clear someone is watching us. Hussam suggests everyone get in the kitchen on the floor where there’s an another story above. The window is blown out, and I realize that one of the perils of being with fighting groups is that you have to go with the flow — even if they have about 20 less years on the front lines than you and they don’t have to catch a plane in a few hours. Then, as I take a photo of a soldier walking in, BAM — the curtains blow in with a cloud of dust.
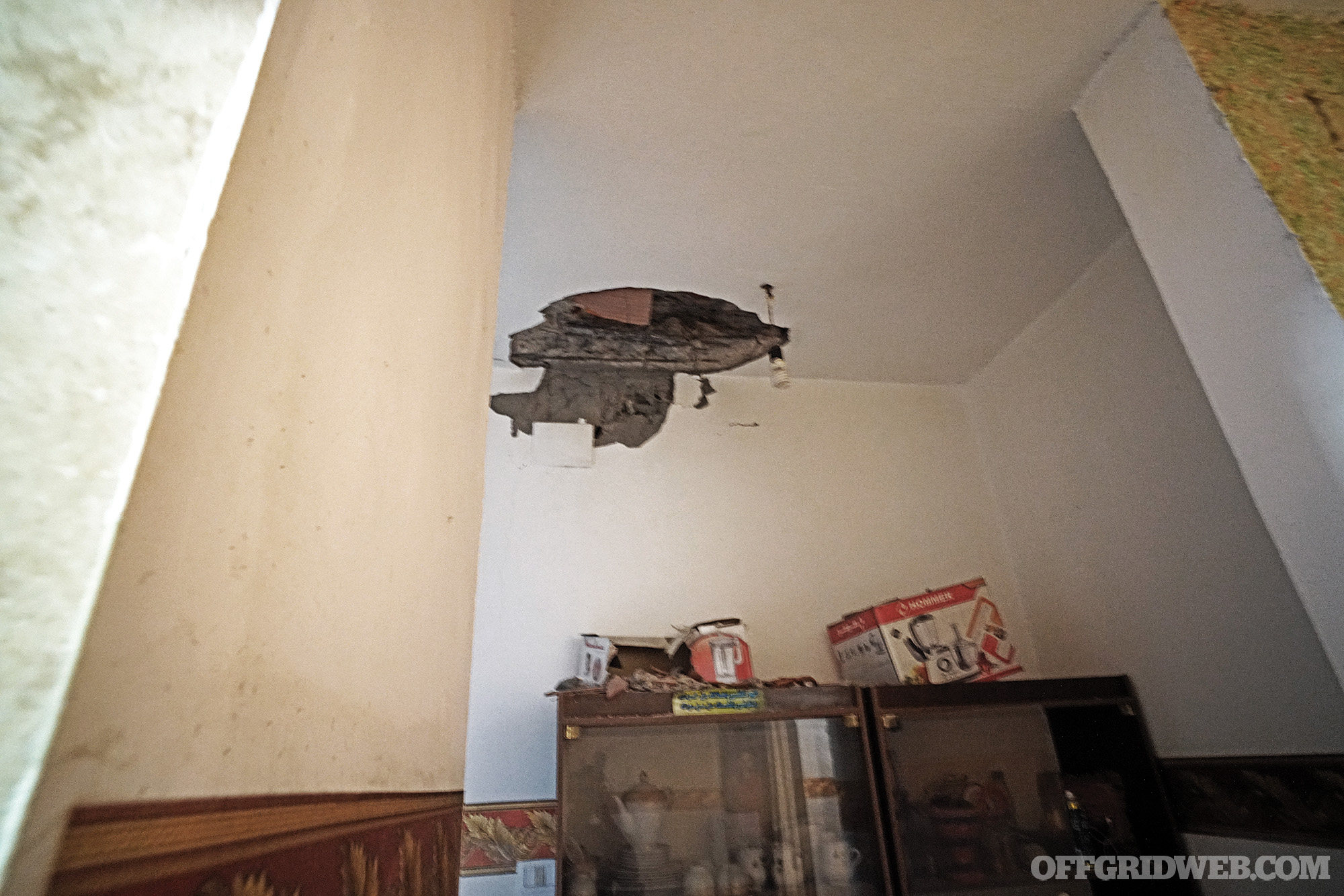

Above: After bracketing our position for hours, the LNA finally got us with an 82mm mortar round dead center.
I decide to go to the center of the house, where the added strength of walls provide the most protection. As I step behind the wall, BANG — the money shot. Right in the living room. Sprayed by plaster and coughing up dust, the soldiers finally decide we should leave. After dropping off the wounded, I catch my scheduled plane to Tunis. That night I’m at the upscale Villa Didon drinking an ice-cold Amstel overlooking the Mediterranean and the ancient city of Carthage. The news says the airport I flew out on was hit by a drone strike 90 minutes after my flight took off. F*ck drones. I order another beer.